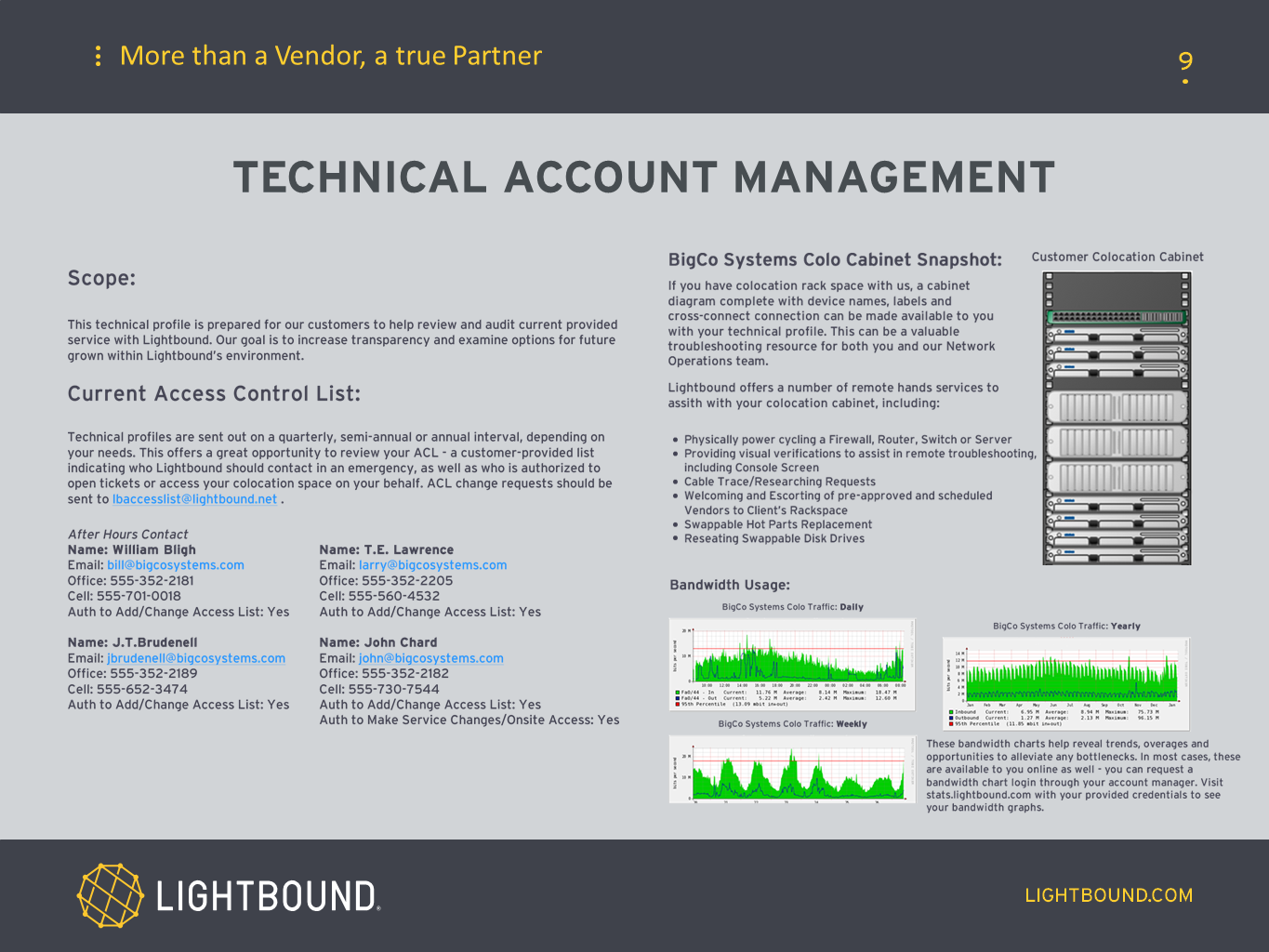
Sales is the heartbeat of every company, and every company wants more.
1.) Development of sales cycle
Accurate forecasting is what every company strives for, but not everyone achieves. The key is knowing where your team is, in all pursuits, and at all times. Identifying the Sales Cycle is the first step in forecasting.
“commit means commit”
Sales Cycle and Forecast Guidelines
2.) forecasting process, tracking and analytics
The images below show the "Stage" progression of the sales cycle from "Visible (10%) to Booked (100%). Notice the probability and the Forecast Category change automatically depending on the change in "Stage", which is the only field that Account Managers have control of.
Note: The opportunities represented are from different companies. The examples are used to illustrate the change in sales cycle "Stage".






3.) Pipeline & pipeline acceleration
One of the first projects when I hired on at LightBound was creating dashboards so the management team could see all the details of each sale and categorize them (Forecasting 1.0 and 2.0 Above). The next project is pictured below, which required the implementation of Cloud9 (now insidesales.com). The product gives us the ability to look at historical changes within each sales pursuit. Notice I don't say "deals" because we aren't selling used cars. All of these fields needed to be created and defined within salesforce.com before I implemented insidesales.com, and before that, I had to create and define the various stages of the sales cycle.
The first graph is a waterfall dashboard that gives me a high level view of what is happening during the quarter as reps move the sales through the sales process. It also highlights any lost sales so we can talk about what happened and what needs to be corrected.
The second graph shows me all the details for each sale in the forecast so I can see which ones might be at risk. Things like number of days in the pipeline, days in each stage, and days since last touch are often training or mentoring opportunities for management to get involved and ask the right questions.
The second graph show me where each individual reps is related to their quota as well as commit, Best Case and Pipeline.



4.) development of corporate powerpoint
The corporate PowerPoint can be used in two primary ways.
1.) As a general overview of your company and your value proposition (TELLING) and 2.) To align the buyers buying criteria to your key value proposition (in other words SELLING!)
To the extent you can align with your buyers buying criteria, buying cycle, their personal and professional win, you have the best chance of engagement. Buying is emotional, and to the extent you can connect with the emotions of key decision makers, the more likely you will be able to position your offering competitively.
This resonated with several prospects during key sales pursuits, in particular with Financial First Credit Union. Used properly, this helps you align your value prop to the decision criteria of the key decision makers and position yourself against the competition. We cal this "setting the table". If done, well, you are essentially setting the RFP requirements and setting the bar for anyone else who might compete for the business. This is where the buyer has that "ah ha" moment and you've made the sale. It's NOT about presenting, demoing, or dropping all your candy in the lobby. It's about "connecting" with the buyers emotions.
...and the key is to do your homework before you present ANYTHING. And when you do present, you'd better find some analogies so that all the buyers can connect to those pieces of your presentation.
5.) Development of sales compensation and incentive plans
One of my first tasks when hired at LightBound was to re-write the compensation plans from top to bottom
The problem: Sales Representatives were not incented to achieve goals that were in-line with overall corporate goals, specifically for new business and for new products within existing accounts.
Comp Plans (KISS)
Keep it simple. Compensation should be easy for reps to understand so they know how and when they are hitting goals, and so it's easy for companies to pay the reps for their accomplishments.
Incentives
Incentives should always be in-line with corporate goals, selling new accounts vs. existing accounts, up-sell for new products within accounts, incentives for new product offerings, and retention and/or contract renewals for current clients. The effort varies significantly and the people you need to hire have different stripes.
Compensation Letters and Agreements
Having everything in writing ensures that there are no surprises. Establishing a baseline for your particular business is the first phase. Once you have a better idea of total revenue and compensation, you can then adjust goals and replicate the model for more sales representatives.
pip plans
Setting expectations and holding salespeople accountable is a must-have. PIP plans are an integral part of the incentive plan. Commission is the carrot and the PIP is the stick. This is the same as having an Up-Front contract with your prospect. Everbody knows what the expectations are, so there's no discussion of where things stand.
6.) rework of pricing models and sku's
The rework of the pricing models entailed establishing the overall MSRP, discount levels, and approval levels. Pricing and discount levels were critical to improved profitability and measurement of each category to determine overall profitability and whether we would increase marketing efforts or exit a category. I coordinated an entire re-work of pricing for 5,000 SKU's with the VP of Product Development. We then had to assign accounting codes to each SKU and distill the SKU's into categories, and then develop a quoting system (Steelbrick), and then a CPQ (Octiv) for the sales reps to use.
Here are some the the first Excel pricing tools we developed.